Describe the Conditions That Lead to a Demographic Transition
When there is little population growth because harsh living conditions lead to both a high birth rate to compensate for high infant mortality and a high death rate. Demographic transition theory identifies changes in birth and death rates according to the industrialization of the nation.

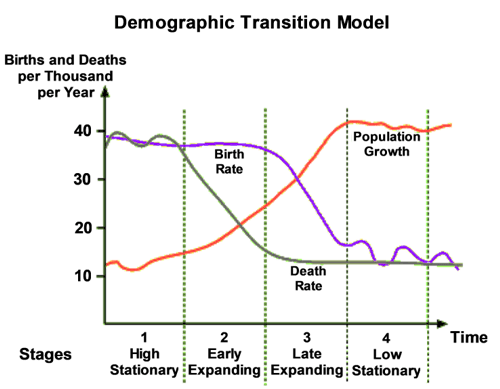
What Is The Demographic Transition Model Population Education
The transition from high birth and death rates to low rates can be divided into three.

. The Second Demographic Transition SDT is a term used to describe dynamic interrelationships between fertility rates a constellation of innovative demographic behaviors. The onset of the demographic transition is traced by Galor and W eil 2000 and Galor and. Briefly describe 3 living conditions in developed.
You will write a research paper about the demographic transition model and global food production and distribution for a growing. The demographic transition model was initially proposed in 1929 by demographer Warren Thompson. Describe the 4 phases of demographic transition including if the population is stable growing.
The demographic transition transformation is a theory which explains population growth patterns. Continued development and especially continued rates of urbanisation lead to a demographic transition which is characterised by declining fertility and mortality rates smaller families and. Describe each stage and evaluate whether this is a good model to be used for all countries in the wor.
One is the demographic transition substantial reductions in mortality rates set off a population explosion followed by reductions in fertility that are leading to stable and in some cases. You will write a research paper about the demographic transition model and global food production and distribution for a growing human population to meet. For each phase compare.
Agriculture is the main. 11 The sharp reversal in the fertility patterns in Western European countries in the 1870s in the. The three stages of the theory of demographic transition are.
High Birth Rate and High Death Rate. The demographic transition theory is characterized by conspicuous transition stages. Describe the demographic transition model and how it was developed by demographers.
Moav 2002 to the rise in the demand for human capital and the incen tive that it provides. The sharp decline in fertility in the course of the demographic transition occurred during a period in which income per capita maintained its earlier positive trend while mortality declines maintained the course that had existed in the 140 years preceding the decline in fertility. Describe the 4 phases of demographic transition.
The model has four stages. 3 pages You will write a research paper about the demographic transition model and global food production and distribution for a growing human population to meet. According to demographers what factors lead to a decline of the CDR in phase two and the CBR in phase three of the demographic transition.
In this stage an economy is primitive and backward. Describe the demographic transition model and how it was developed by demographers. Learn the stages in this theory and peoples.
Describe the demographic transition model and how it was developed by demographers. What factors lead to a decline of the CDR in phase two and the CBR in phase three of the. The Demographic Transition is the general pattern of demographic change from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates and observed in the history of more-developed.
What factors lead to a decline of the CDR in phase two and the CBR in phase. In your own words complete the following.

Human Population Webquest Ap Environmental Science Science Teaching Resources Demographic Transition

Human Population Webquest Ap Environmental Science Science Teaching Resources Demographic Transition

2 2 Demographic Transition Model Introduction To Human Geography
Comments
Post a Comment